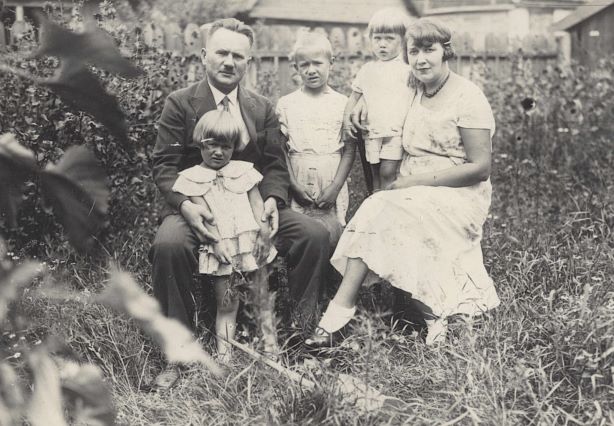
On the morning of 13 April 1940, NKVD soldiers came banging against the doors of the homes of more than 60,000 residents of eastern Poland. They ordered them to pack quickly and loaded them into cattle wagons.
On 22 October 1939 the Soviets organised elections of delegates to the so-called people’s assemblies in the annexed Eastern Borderlands (Kresy) of the Second Polish Republic. After a rapid propaganda campaign accompanied by terror and violence, the “vote” took place.
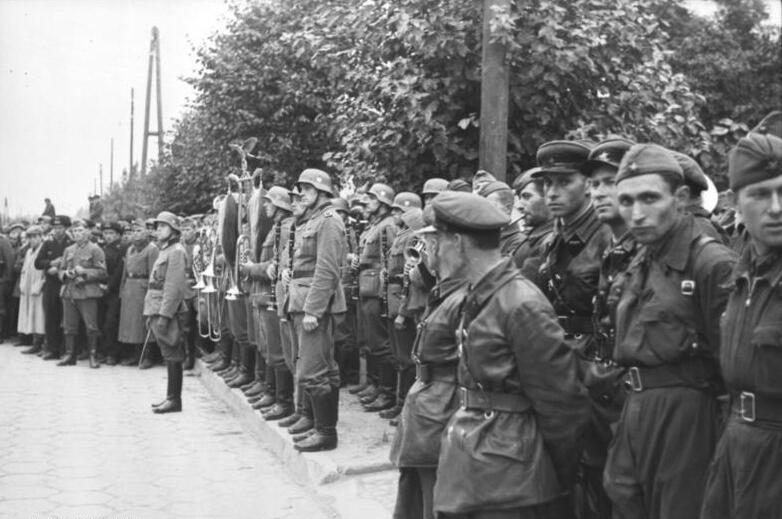
The parade on Unia Lubelska Street in Brest began at 4pm on 22 September 1939 and lasted only about 45 minutes. That was enough time to show the whole world the newly formed alliance of the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany.
The Soviet Union's invasion of Poland on 17 September 1939 came as a shock to Polish society. For several days the country had been defending itself against the German invasion.
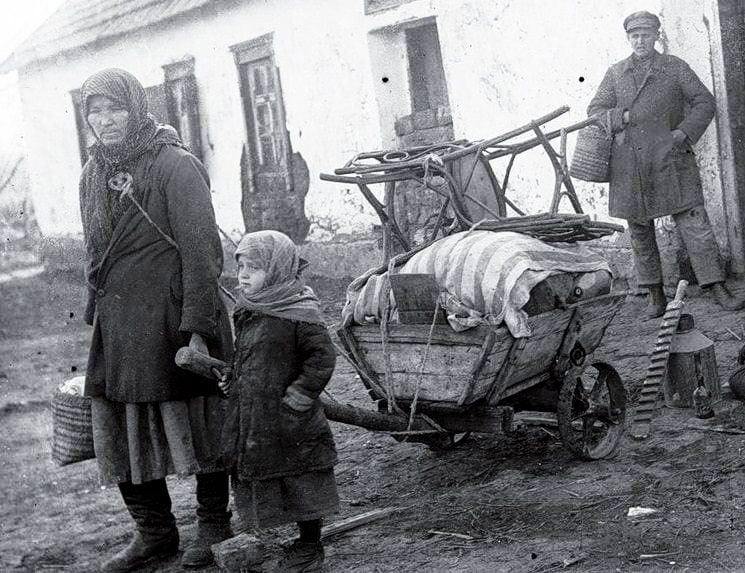
On 30 January 1930, the Politburo of the Central Committee of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks) decided to launch the largest resettlement operation in the entire history of the Soviet Union, still referred to today as the 'kulak deportation'.
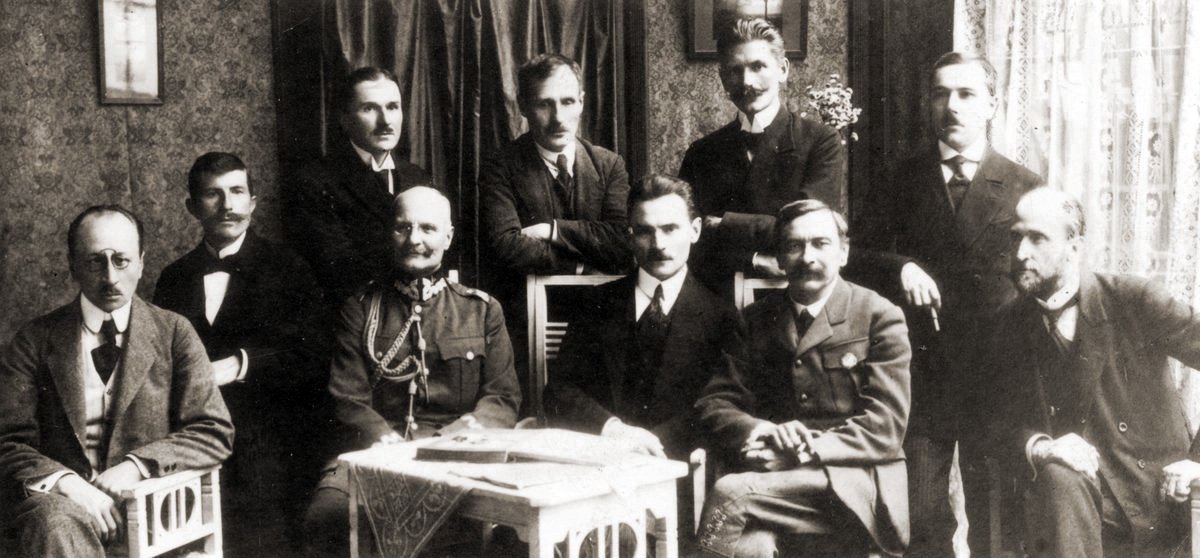
On 18 March 1921, the treaty ending the Polish-Bolshevik war (the so-called Treaty of Riga) was signed in Riga.